Seismic Studies in Carbon Sequestration for Enhanced Oil Recovery
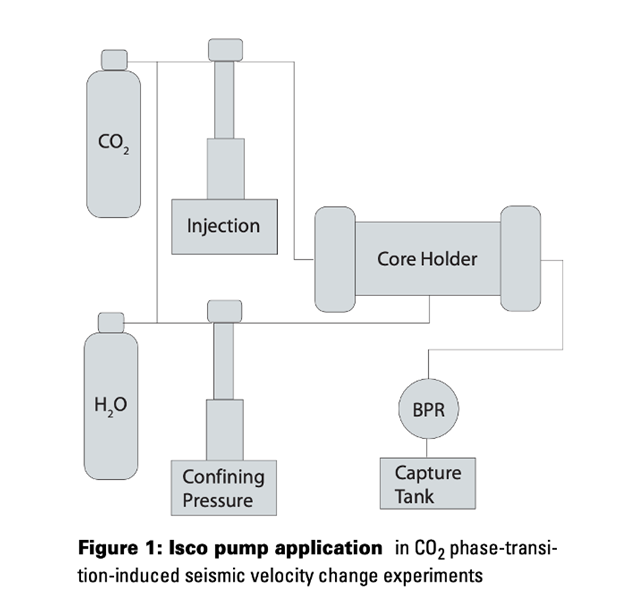
Both CO₂-based enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and CO₂ geological sequestration involve injecting CO₂ into deep rocks. Currently, it is unclear what the short and long term effects may be, or what changes may occur in these rocks, as a result of injecting CO₂, especially if the rocks are composed of carbonates. At the University of North Dakota Petroleum Engineering Lab, Teledyne Isco syringe pumps were used to provide needed pressures to simulate conditions encountered in deep petroleum reservoirs and saline aquifers, and to control flow rates accurately during experimental investigation of CO₂ phase–transition-induced seismic velocity changes.
Figure 1: Isco pump application in C0₂ phase-transition-induced seismic velocity change experiments
University of North Dakota, Grand Forks, ND 58202 USA