【ISCO】AN42 _ 相關地質碳封存條件之反應 (Conducting Batch Reactions at Relevant Geologic Carbon Sequestration Condtions)
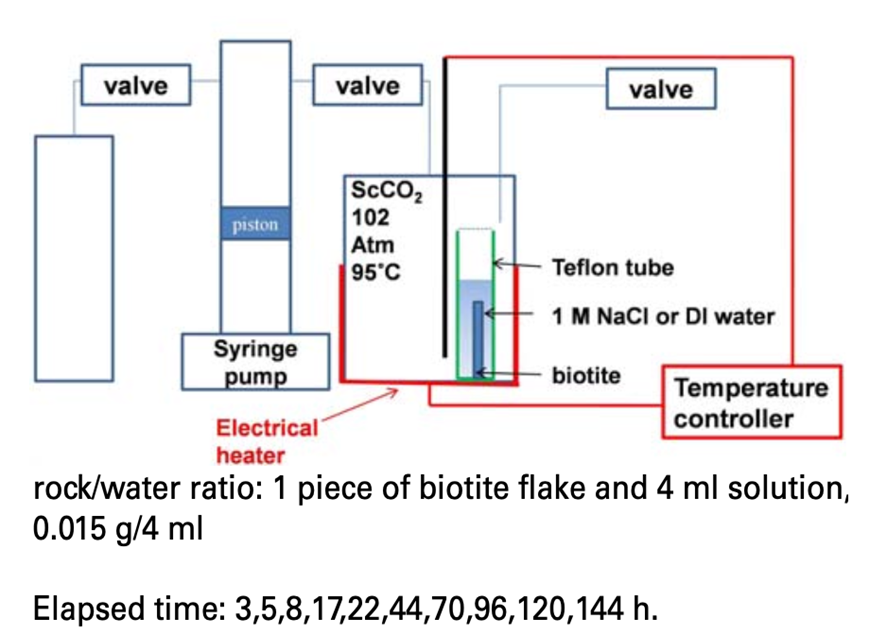
Geologic carbon sequestration (GCS) is needed to mitigate global warming caused by increased atmo- spheric CO₂ concentrations.

Geologic carbon sequestration (GCS) is needed to mitigate global warming caused by increased atmo- spheric CO₂ concentrations.
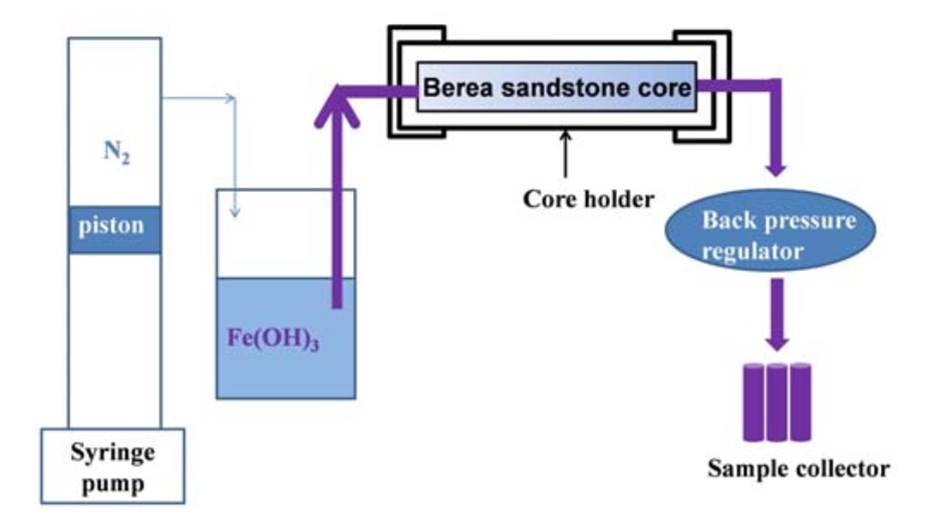
Iron hydroxide precipitation is an important process in many subsurface environments, such as managed aquifer recharge, geologic carbon sequestration, as well as water injection enhanced oil production.
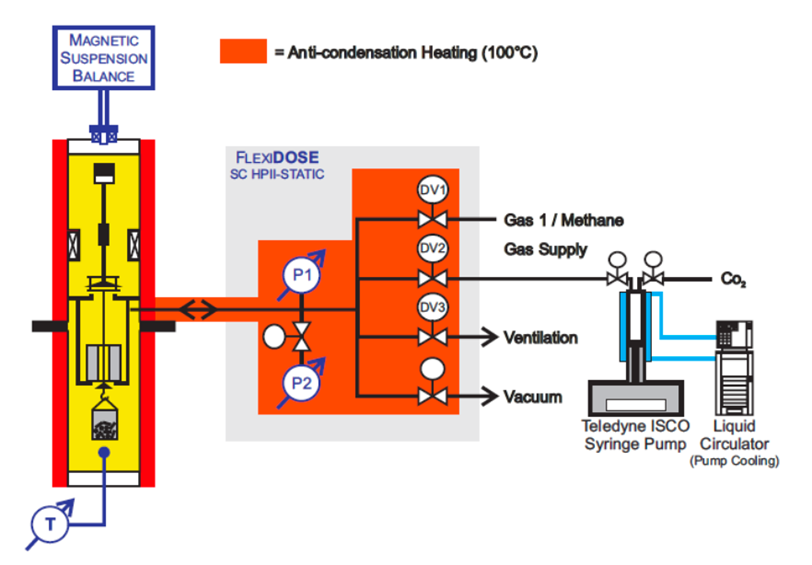
Coal bed methane is a promising alternative to con- ventional gas. Enhanced Coal Bed Methane (ECBM) technology combines improved methane recovery with underground storage of CO₂.
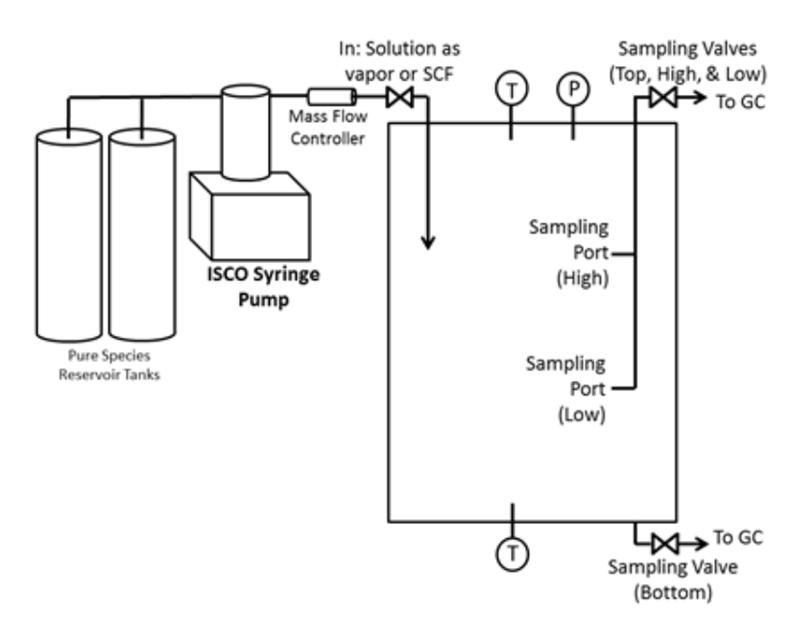
Supercritical fluids exist at high pressures and offer potential for effective and efficient separations. This investigation involves exploring the equilibrium behavior of supercritical fluid mixtures with two or more species, one being carbon dioxide (CO₂).
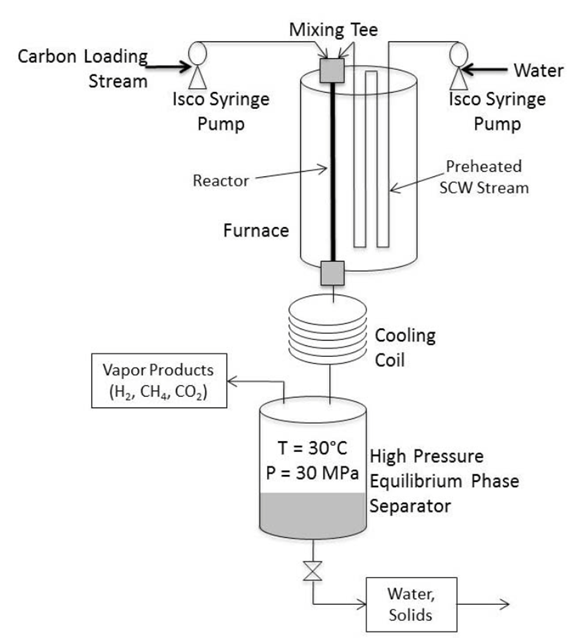
Gasification of biomass involves thermal decomposi- tion of organic components in the absence of oxygen. Supercritical water (SCW) is an excellent reaction media to gasify biomass.
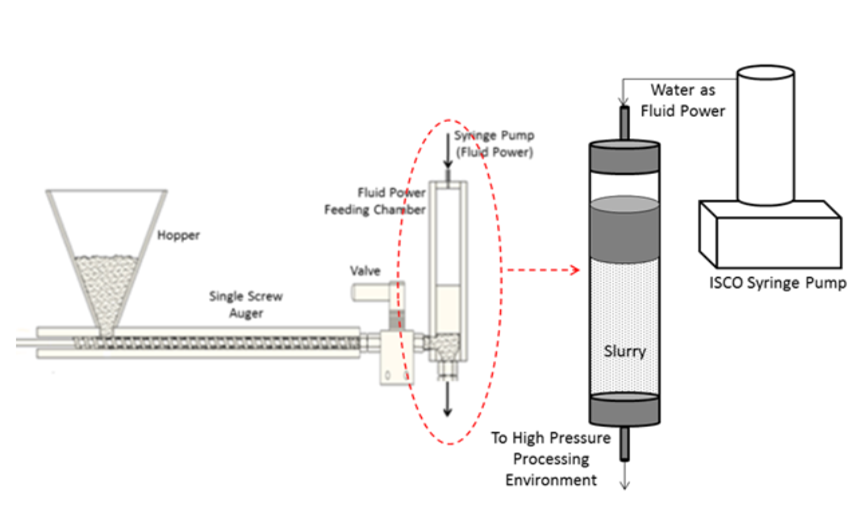
Supercritical fluids provide unique opportunities for processing and separations of biomass and other carbo- naceous materials. Continuous operation, rather than batch processing, is necessary for supercritical fluid technology to be used on a large scale.
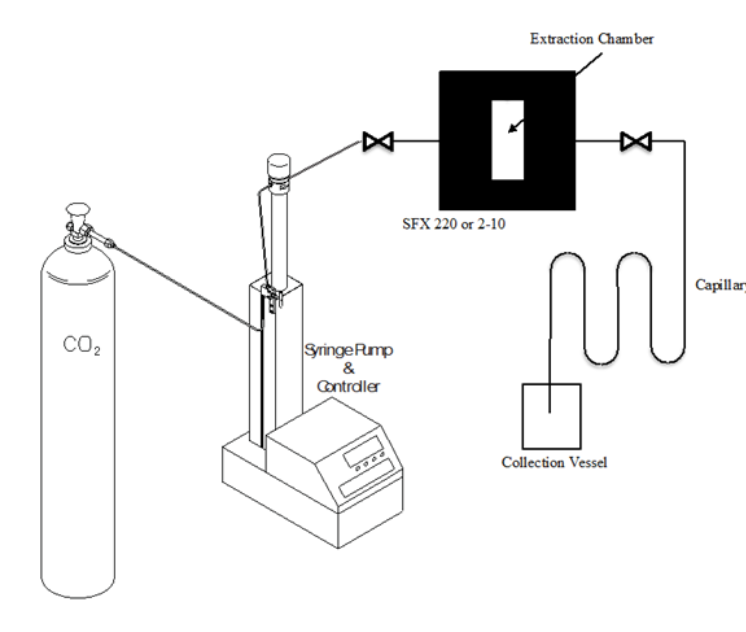
Soybean oil is one of the most widely used plant oils today. Most soybean oil is extracted using hexane solvent extraction; while being fast and efficient, this has several disadvantages.
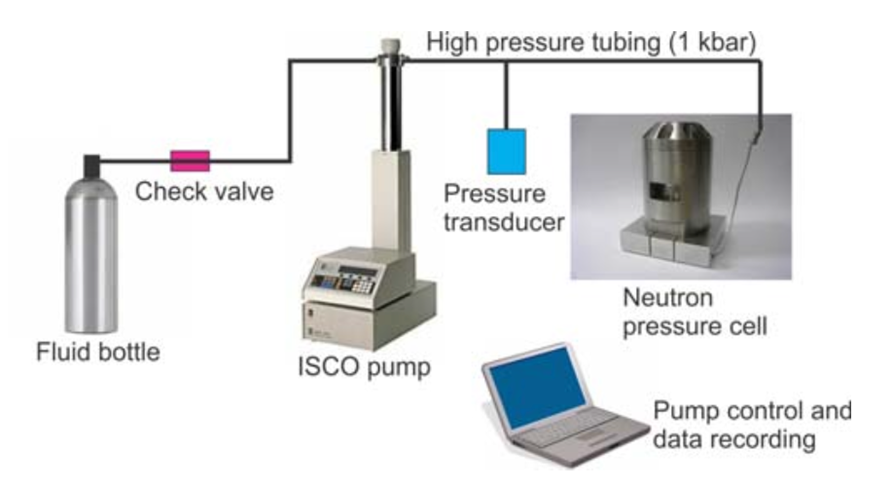

To better understand fluid migration through porous rock formations and fluid reservoir processes, a nanoscale quantitative understanding of fluid-mineral interactions is needed, which can be obtained from combined excess sorption and neutron scattering experiments.
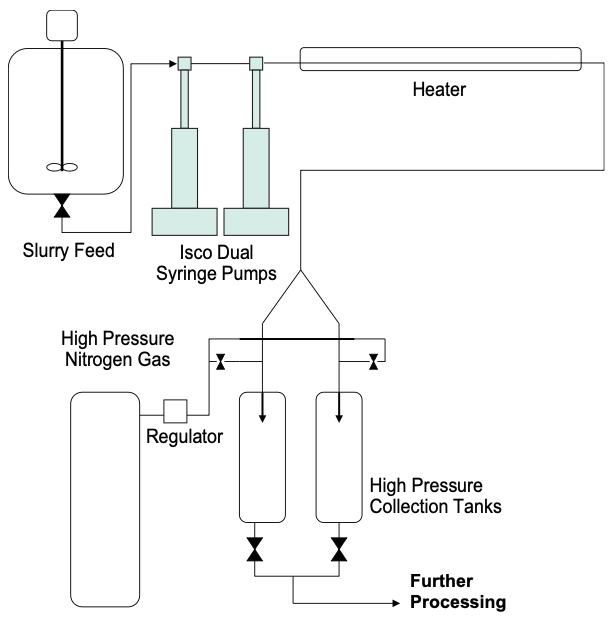
The present investigation pertains to the processing of biomass with an aqueous mixture with and without the presence of a catalyst to form cleaved biopolymer byproducts.
Biomass substrates such as switch grass and corn stover are now commonly used in the production of bio- fuels.